FabulousFusionFood's European Recipes Home Page
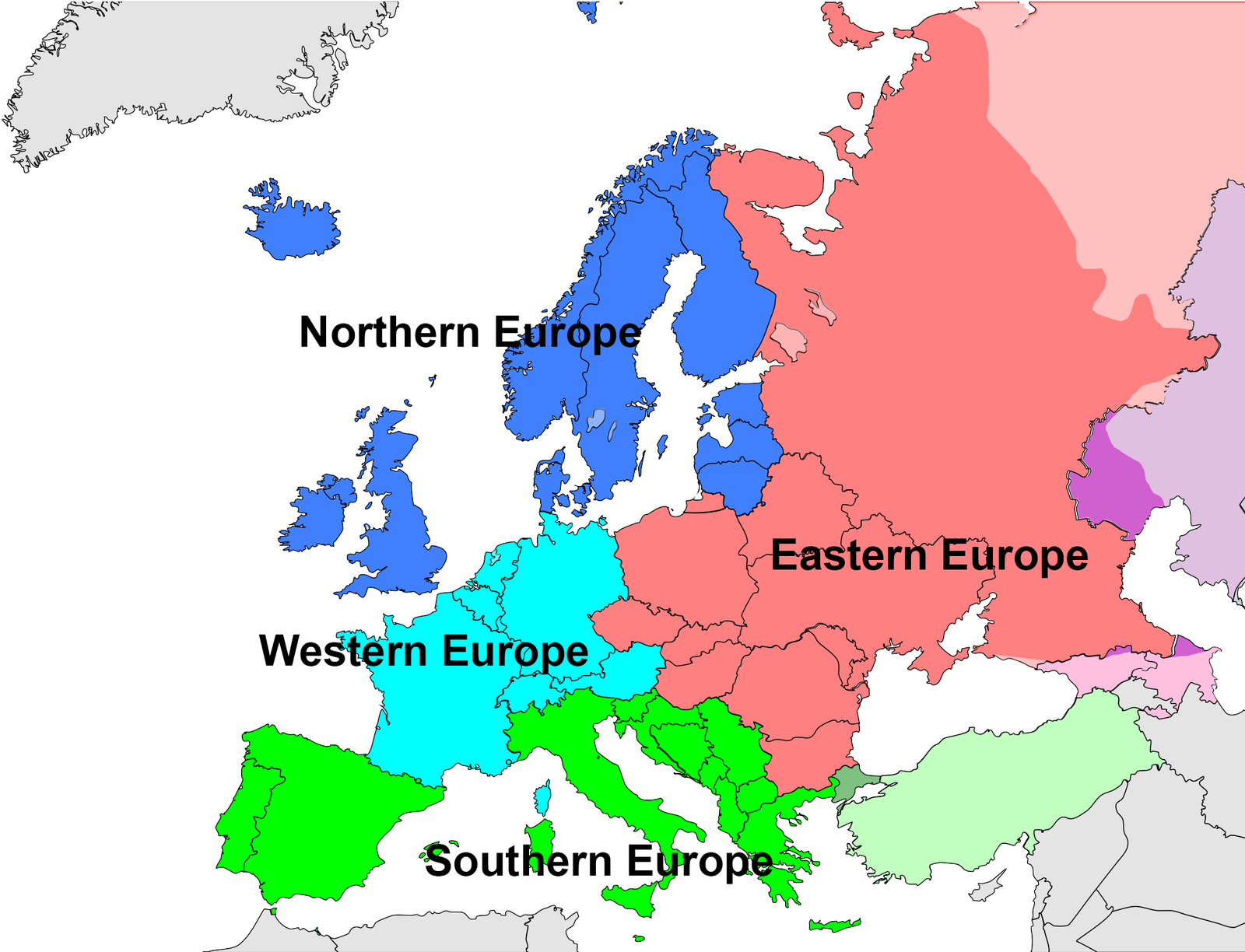 The map of Europe with the four regions of Europe, according to the UN geoscheme
The map of Europe with the four regions of Europe, according to the UN geoschemeclassification, shown.
Welcome to the summary page for FabulousFusionFood's European recipes. This page provides links to all the European recipes presented on this site, with 5404 recipes in total.
These recipes, for the major part, originate in the Europe. Otherwise they are fusion recipes with major European influences.
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Asia and Africa. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus Strait
Europe covers about 10.18 million km2 (3.93 million sq mi), or 2% of Earth's surface (6.8% of land area), making it the second-smallest continent (using the seven-continent model). Politically, Europe is divided into about fifty sovereign states, of which Russia is the largest and most populous, spanning 39% of the continent and comprising 15% of its population. Europe had a total population of about 745 million (about 10% of the world population) in 2021; the third-largest after Asia and Africa. The European climate is affected by warm Atlantic currents, such as the Gulf Stream, which produce a temperate climate, tempering winters and summers, on much of the continent. Further from the sea, seasonal differences are more noticeable producing more continental climates.
European culture consists of a range of national and regional cultures, which form the central roots of the wider Western civilisation, and together commonly reference ancient Greece and ancient Rome, particularly through their Christian successors, as crucial and shared roots. Beginning with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE, Christian consolidation of Europe in the wake of the Migration Period marked the European post-classical Middle Ages. The Renaissance spread in the continent a new humanist interest in art and science. Since the Age of Discovery, led by Spain and Portugal, Europe played a predominant role in global affairs with multiple explorations and conquests around the world. Between the 16th and 20th centuries, European powers colonised at various times the Americas, almost all of Africa and Oceania, and the majority of Asia.
The Age of Enlightenment, the French Revolution, and the Napoleonic Wars shaped the continent culturally, politically, and economically from the end of the 17th century until the first half of the 19th century. The Industrial Revolution, which began in Great Britain at the end of the 18th century, gave rise to radical economic, cultural, and social change in Western Europe and eventually the wider world. Both world wars began and were fought to a great extent in Europe, contributing to a decline in Western European dominance in world affairs by the mid-20th century as the Soviet Union and the United States took prominence and competed over dominance in Europe and globally. The resulting Cold War divided Europe along the Iron Curtain, with NATO in the West and the Warsaw Pact in the East. This divide ended with the Revolutions of 1989, the fall of the Berlin Wall, and the dissolution of the Soviet Union, which allowed European integration to advance significantly.
The place name Evros was first used by the ancient Greeks to refer to their northernmost province, which bears the same name today. The principal river there – Evros (today's Maritsa) – flows through the fertile valleys of Thrace,[18] which itself was also called Europe, before the term meant the continent.
In classical Greek mythology, Europa (Ancient Greek: Εὐρώπη, Eurṓpē) was a Phoenician princess. One view is that her name derives from the Ancient Greek elements εὐρύς (eurús) 'wide, broad', and ὤψ (ōps, gen. ὠπός, ōpós) 'eye, face, countenance', hence their composite Eurṓpē would mean 'wide-gazing' or 'broad of aspect'. Broad has been an epithet of Earth herself in the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European religion and the poetry devoted to it.[20] An alternative view is that of Robert Beekes, who has argued in favour of a pre-Indo-European origin for the name, explaining that a derivation from eurus would yield a different toponym than Europa. Beekes has located toponyms related to that of Europa in the territory of ancient Greece, and localities such as that of Europos in ancient Macedonia.
Europe is generally divided into the regions: Northern Europe, Eastern Europe, Southern Europe and Western Europe, There is also the historical region of Central Europe. Though the Mediterranean region also covers North Africa and part of Western Asia, it must be remembered that Europe represents the northern part of the Mediterranean Region, which is why I'm including links to that region on this page.
The term 'Central Europe' is often used by historians to designate states formerly belonging to the Holy Roman Empire, the Habsburg Empire, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
These recipes, for the major part, originate in the Europe. Otherwise they are fusion recipes with major European influences.
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Asia and Africa. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus Strait
Europe covers about 10.18 million km2 (3.93 million sq mi), or 2% of Earth's surface (6.8% of land area), making it the second-smallest continent (using the seven-continent model). Politically, Europe is divided into about fifty sovereign states, of which Russia is the largest and most populous, spanning 39% of the continent and comprising 15% of its population. Europe had a total population of about 745 million (about 10% of the world population) in 2021; the third-largest after Asia and Africa. The European climate is affected by warm Atlantic currents, such as the Gulf Stream, which produce a temperate climate, tempering winters and summers, on much of the continent. Further from the sea, seasonal differences are more noticeable producing more continental climates.
European culture consists of a range of national and regional cultures, which form the central roots of the wider Western civilisation, and together commonly reference ancient Greece and ancient Rome, particularly through their Christian successors, as crucial and shared roots. Beginning with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE, Christian consolidation of Europe in the wake of the Migration Period marked the European post-classical Middle Ages. The Renaissance spread in the continent a new humanist interest in art and science. Since the Age of Discovery, led by Spain and Portugal, Europe played a predominant role in global affairs with multiple explorations and conquests around the world. Between the 16th and 20th centuries, European powers colonised at various times the Americas, almost all of Africa and Oceania, and the majority of Asia.
The Age of Enlightenment, the French Revolution, and the Napoleonic Wars shaped the continent culturally, politically, and economically from the end of the 17th century until the first half of the 19th century. The Industrial Revolution, which began in Great Britain at the end of the 18th century, gave rise to radical economic, cultural, and social change in Western Europe and eventually the wider world. Both world wars began and were fought to a great extent in Europe, contributing to a decline in Western European dominance in world affairs by the mid-20th century as the Soviet Union and the United States took prominence and competed over dominance in Europe and globally. The resulting Cold War divided Europe along the Iron Curtain, with NATO in the West and the Warsaw Pact in the East. This divide ended with the Revolutions of 1989, the fall of the Berlin Wall, and the dissolution of the Soviet Union, which allowed European integration to advance significantly.
The place name Evros was first used by the ancient Greeks to refer to their northernmost province, which bears the same name today. The principal river there – Evros (today's Maritsa) – flows through the fertile valleys of Thrace,[18] which itself was also called Europe, before the term meant the continent.
In classical Greek mythology, Europa (Ancient Greek: Εὐρώπη, Eurṓpē) was a Phoenician princess. One view is that her name derives from the Ancient Greek elements εὐρύς (eurús) 'wide, broad', and ὤψ (ōps, gen. ὠπός, ōpós) 'eye, face, countenance', hence their composite Eurṓpē would mean 'wide-gazing' or 'broad of aspect'. Broad has been an epithet of Earth herself in the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European religion and the poetry devoted to it.[20] An alternative view is that of Robert Beekes, who has argued in favour of a pre-Indo-European origin for the name, explaining that a derivation from eurus would yield a different toponym than Europa. Beekes has located toponyms related to that of Europa in the territory of ancient Greece, and localities such as that of Europos in ancient Macedonia.
Europe is generally divided into the regions: Northern Europe, Eastern Europe, Southern Europe and Western Europe, There is also the historical region of Central Europe. Though the Mediterranean region also covers North Africa and part of Western Asia, it must be remembered that Europe represents the northern part of the Mediterranean Region, which is why I'm including links to that region on this page.
Northern Europe
| Arms | Flag | Name of Territory | Capital | Name in Official Language(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Åland | Mariehamn | Landskapet Åland (Swedish)/Ahvenanmaan maakunta (Finnish) | ||
| Channel Islands (UK) | Saint Peter Port/Saint Helier | Channel Islands/les Anglo-Normandes (French)/Îles d'la Manche (Norman) | ||
| Denmark | Copenhagen | Danmark | ||
| Estonia | Tallinn | Eesti Vabariik | ||
| Faroe Islands (Denmark) | Tórshavn | Føroyar (Faroese)/Færøerne (Danish) | ||
| Finland | Halsinki | Suomen tasavalta | ||
| Iceland | Reykjavik | Ísland | ||
| Republic of Ireland | Dublin | Éire | ||
| Isle of Man | Douglas | Mannin, Ellan Vannin | ||
| Latvia | Riga | Latvijas Republika (Latvian)/Latvejas Republika (Latgalian)/ Lețmō Vabāmō (Livonian) |
||
| Lithuania | Vilnius | Lietuvos Respublika | ||
| Norway | Oslo | Kongeriket Norge (Bokmål)/Kongeriket Noreg (Nynorsk) | ||
| Svalbard and Jan Mayen (Denmark) | Longyearbyen | |||
| Sweden | Stockholm | Konungariket Sverige | ||
| United Kingdom | London | United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
Eastern Europe
| Arms | Flag | Name of Territory | Capital | Name in Official Language(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abkhazia | Sukhumi | Аԥсны Аҳәынҭқарра (Abkhaz)/ Республика Абхазия (Russian) |
||
| Albania | Tirana | Republika e Shqipërisë (Albanian) | ||
| Belarus | Minsk | Рэспубліка Беларусь (Belarusian)/ Республика Беларусь (Russian) |
||
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Sarajevo | Bosna i Hercegovina Serbo-Croatian (Latin)/ Босна и Херцеговина Serbo-Croatian (Cyrillic) |
||
| Bulgaria | Sofia | Република България (Republika Bŭlgariya) | ||
| Czech Republic | Prague | Czech Republic/Česká republika (Czech) | ||
| Hungary | Budapest | Magyarország (Hungarian) | ||
| Kosovo | Pristina | Republika e Kosovës (Albanian) Република Косово / Republika Kosovo (Serbian) | ||
| Moldova | Chișinău | Republica Moldova (Romanian) | ||
| Montenegro | Podgorica | Crna Gora, Црна Гора (Montenegrin) | ||
| North Macedonia | Skopje | Република Северна Македонија (Macedonian)/Republika e Maqedonisë së Veriut (Albanian) | ||
| Poland | Warsaw | Rzeczpospolita Polska (Polish) | ||
| Romania | Bucharest | România (Romanian) | ||
| Russia | Moscow | Russian Federation/Российская Федерация (Russian) | ||
| Serbia | Belgrade | Republic of Serbia/Република Србија, Republika Srbija (Serbian) | ||
| Slovakia | Bratislava | Slovak Republic/Slovenská republika (Slovak) | ||
| Slovenia | Ljubljana | Republika Slovenija | ||
| Transnistria | Tiraspol | Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic | ||
| Turkey (East Thrace) | Ankara | Republic of Türkiye/Türkiye Cumhuriyeti (Turkish) | ||
| Ukraine | Kyiv | Україна (Ukrainian) |
Central Europe
| Arms | Flag | Name of Territory | Capital | Name in Official Language(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Czech Republic | Prague | Czech Republic/Česká republika (Czech) | ||
| Croatia | Zagreb | Republika Hrvatska (Croatian) | ||
| Hungary | Budapest | Magyarország (Hungarian) | ||
| Lithuania | Vilnius | Republic of Lithuania/Lietuvos Respublika (Lithuanian) | ||
| Poland | Warsaw | Rzeczpospolita Polska (Polish) | ||
| Romania | Bucharest | România (Romanian) | ||
| Slovakia | Bratislava | Slovak Republic/Slovenská republika (Slovak) | ||
| Slovenia | Ljubljana | Republic of Slovenia Republika Slovenija (Slovene) |
Southern Europe
| Arms | Flag | Name of Territory | Capital | Name in Official Language(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albania | Tirana | Republic of Albania/Republika e Shqipërisë (Albanian) | ||
| Andorra | Andorra la Vella | Principality of Andorra/Principat d'Andorra (Catalan) | ||
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Sarajevo | Bosnia and Herzegovina/Serbo-Croatian (Latin): Bosna i Hercegovina/ Serbo-Croatian (Cyrillic): Босна и Херцеговина |
||
| Croatia | Zagreb | Republic of Croatia/Republika Hrvatska (Croatian) | ||
| Cyprus | Nicosia | Republic of Cyprus/Κυπριακή Δημοκρατία (Greek)/ Kıbrıs Cumhuriyeti (Turkish) |
||
| Gibraltar | Gibraltar | Gibraltar | ||
| Greece | Athens | Hellenic Republic/Ελληνική Δημοκρατία ([Ellinikí Dimokratía] Greek) | ||
| Holy See/Vatican City | Vatican City | Vatican City State/Stato della Città del Vaticano (Italian)/ Status Civitatis Vaticanae (Latin) |
||
| Italy | Rome | Italian Republic/Repubblica Italiana (Italian) | ||
| Malta | Valletta | Republic of Malta/Repubblika ta' Malta (Maltese) | ||
| Montenegro | Podgorica | Montenegro/Crna Gora, Црна Гора (Montenegrin) | ||
| North Macedonia | Skopje | Republic of North Macedonia/Република Северна Македонија (Macedonian)/ Republika e Maqedonisë së Veriut (Albanian) |
||
| Portugal | Lisbon | Portuguese Republic/República Portuguesa (Portuguese) | ||
| San Marino | San Marino | Republic of San Marino/Repubblica di San Marino (Italian) | ||
| Serbia | Belgrade | Republic of Serbia/Република Србија, Republika Srbija (Serbian) | ||
| Slovenia | Ljubljana | Republic of Slovenia/Republika Slovenija (Slovene) | ||
| Spain | Madrid | Kingdom of Spain/Reino de España (Spanish) |
Western Europe
| Arms | Flag | Name of Territory | Capital | Name in Official Language(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | Vienna | Republic of Austria/Republik Österreich (German) | ||
| Belgium | Brussels | Kingdom of Belgium/Koninkrijk België (Dutch)/ Royaume de Belgique (French)/Königreich Belgien (German) |
||
| France | Prais | French Republic/République française (French) | ||
| Germany | Berlin | Federal Republic of Germany/Bundesrepublik Deutschland (German) | ||
| Liechtenstein | Vaduz | Principality of Liechtenstein/Fürstentum Liechtenstein (German) | ||
| Luxembourg | Luxembourg City | Grand Duchy of Luxembourg/Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg (Luxembourgish)/ Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (French)/Großherzogtum Luxemburg (German) |
||
| Monaco | Monaco | Principality of Monaco/Principauté de Monaco (French)/ Prinçipatu de Mùnegu (Monégasque) |
||
| the Netherlands | Amsterdam | Nederland (Dutch) | ||
| Switzerland | Zurich | Swiss Federation/Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft (German)/Confédération suisse (French)/ Confederazione Svizzera (Italian)/Confederaziun svizra (Romansh)/ Confoederatio helvetica (Latin) |
The alphabetical list of all the European recipes on this site follows, (limited to 100 recipes per page). There are 5404 recipes in total:
Page 1 of 55
Page 1 of 55