FabulousFusionFood's Goat-based Recipes Home Page
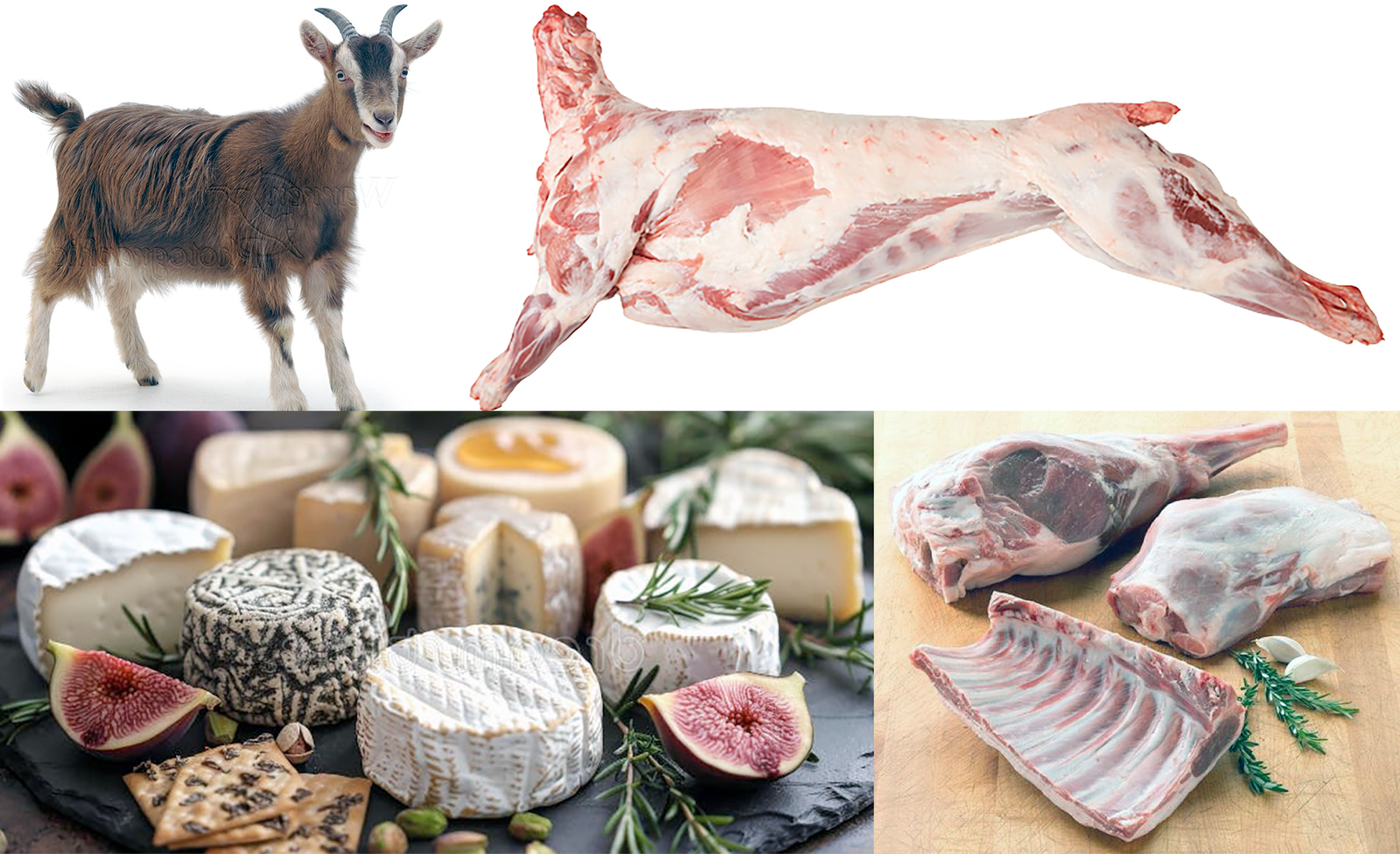 Clockwise from top left: Goat, prepared kid goat, goat meat selection, goat cheese selection.
Clockwise from top left: Goat, prepared kid goat, goat meat selection, goat cheese selection.
Welcome to FabulousFusionFood's Goat-based Recipes Page — The domestic goat, Capra hircus is a species of goat-antelope that is mostly kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (C. aegagrus) of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the Bovidae (cow) family and the subfamily, Caprinae, meaning it is closely related to the sheep. It was one of the first animals to be domesticated, in Iran around 10,000 years ago.
Goats have been used for milk, meat, wool, and skins across much of the world. Milk from goats is often turned into cheese. In 2022, there were more than 1.1 billion goats living in the world, of which 150 million were in India.
Goats are among the earliest animals to have been domesticated by humans. A genetic analysis confirms the archaeological evidence that the wild bezoar ibex, found today in the Zagros Mountains, but formerly widespread in Anatolia, is the likely original ancestor of all or most domestic goats today.
Neolithic farmers began to herd wild goats primarily for easy access to milk and meat, as well as to their dung, which was used as fuel; and their bones, hair, and sinew were used for clothing, building, and tools. The earliest remnants of domesticated goats dating 10,000 years Before Present are found in Ganj Dareh in Iran. Goat remains have been found at archaeological sites in Jericho, Choga Mami, Djeitun, and Çayönü, dating the domestication of goats in Western Asia at between 8,000 and 9,000 years ago. DNA evidence suggests that goats were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Historically, goat hide has been used for water and wine bottles in both traveling and transporting wine for sale, and to produce parchment.
Goats are ruminants. They have a four-chambered stomach consisting of the rumen, the reticulum, the omasum, and the abomasum. As with other mammal ruminants, they are even-toed ungulates. The females have an udder consisting of two teats, in contrast to cattle, which have four teats. An exception to this is the Boer goat, which sometimes may have up to eight teats. Goats are diploid with two sets of 30 chromosomes.
The Modern English word goat comes from Old English gāt "goat, she-goat", which in turn derives from Proto-Germanic *gaitaz (cf. Dutch/Frisian/Icelandic/Norwegian geit, German Geiß, and Gothic gaits), ultimately from Proto-Indo-European *ǵʰaidos meaning "young goat" (cf. Latin haedus "kid"). To refer to the male goat, Old English used bucca (cf. Dutch/Frisian bok, modern English buck) until ousted by hegote, hegoote ('he-goat') in the late 12th century. Nanny goat (adult female) originated in the 18th century, and billy goat (adult male) in the 19th century. Female goats, like other various animals, are also called does. Castrated males are called wethers. While the words hircine and caprine both refer to anything having a goat-like quality, hircine is used most often to emphasize the distinct smell of domestic goats.
Juvenile goats are called kids, a term derived from Old Norse kið, with the same meaning. It has been a slang term for human children since the 1590s, and established as an informal term since the 1840s.
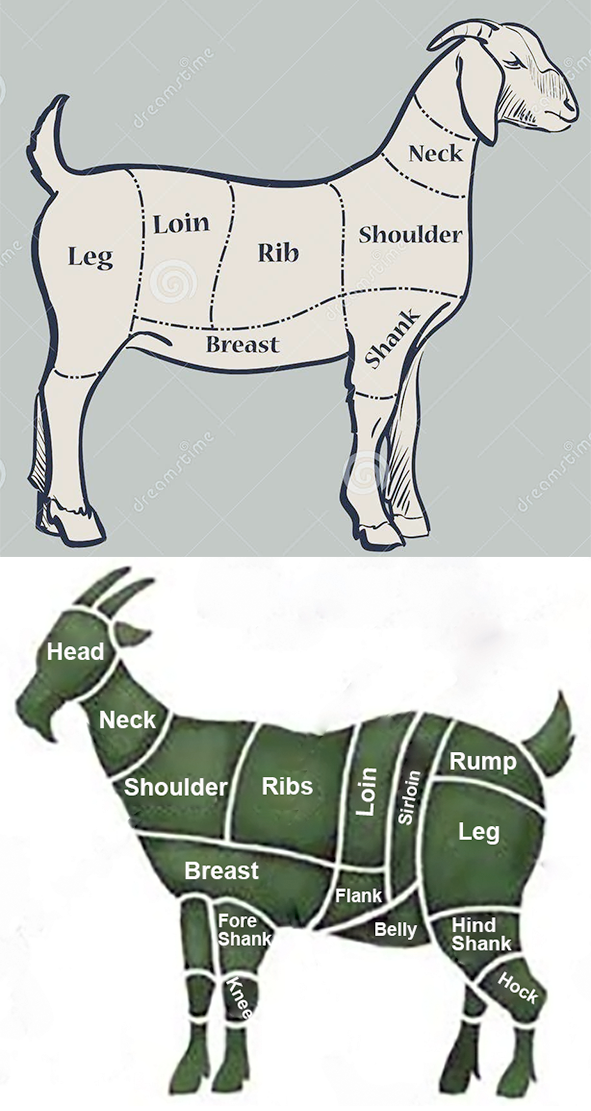 Typical cuts of goat meat, with those for kid goat shown top and a
Typical cuts of goat meat, with those for kid goat shown top and amore mature animal, bottom.
Goat meat is both a staple and a delicacy in the world's cuisines. The cuisines best known for their use of goat include African cuisine, Middle Eastern, Indian, Indonesian, Nepali, Bangladeshi, Pakistani, Abruzzese, Mexican, Caribbean (Jamaica), Haitian cuisine, Dominican cuisine and Ecuadorian. Cabrito, which is baby goat, is a typical food of Monterrey, Nuevo León, Mexico; in Italy it is called "capretto". Goat meat can be prepared in a variety of ways, such as being stewed, curried, baked, grilled, barbecued, minced, canned, fried, or made into sausage. Goat jerky is another popular variety.
Goat has a reputation for having a strong, gamey flavour, but the taste can also be mild, depending on how it is raised and prepared. Caribbean cultures often prefer meat from mature goats, which tends to be more pungent (which is why the meat is first cleaned in a blend of lime juice and water there and it's pre-boiled with the initial boiling liquid discarded), while some other cultures prefer meat that comes from younger goats that are six to nine months old. Ribs, loins, and tenderloin goat meat are suitable for quick cooking, while other cuts are best for long braising. Despite being classified as red meat, goat is leaner and contains less cholesterol and fat than both lamb and beef, and less energy than beef and lamb; therefore, it requires low-heat, slow cooking to preserve tenderness and moisture.
Goat meat cuts tend to be very similar to lamb/sheep cuts (see image) and the cuts are often cooked in similar ways. Though there are some differences in the cuts between kid goats and older goats due to the respective sizes of the animals.
The alphabetical list of all the goat-based recipes on this site follows, (limited to 100 recipes per page). There are 241 recipes in total:
Page 1 of 3
| Afghan Kofta Curry Origin: Afghanistan | Cabri Massalé (Kid Goat Massala) Origin: Reunion | Dominica Sancocho Origin: Dominica |
| Afia Efere (White Soup) Origin: Nigeria | Cabrito com Inhame (Kid Goat with Yam) Origin: Cape Verde | Domoda II Origin: Gambia |
| Aliter Haedinam sive Agninam Excaldatam (Roast Kid or Lamb) Origin: Roman | Cachupa Rica Origin: Cape Verde | Dopiazeh Origin: Iran |
| Aliter Haedinam sive Agninam Excaldatam (Stew of Kid or Lamb) Origin: Roman | Cachupa Rica Origin: Cape Verde | Efere Usung Udia Origin: Nigeria |
| Aliter Haedinam sive Agninam Excaldatam (Stew of Kid or Lamb, Another Way) Origin: Roman | Calalou (Beninese Callaloo) Origin: Benin | Egredouce (Meat in Sweet and Sour Sauce) Origin: England |
| Aliter Haedum sive Agnum Assum (Roast Kid or Lamb, Another Way) Origin: Roman | Caldeiraa de Cabrito (Goat Meat Stew) Origin: Mozambique | Fah-Fah (Soupe Djiboutienne) Origin: Djibouti |
| Aliter Haedus sive Agnus Syringiatus (Boned Suckling Kid or Lamb, Another Way) Origin: Roman | Calulu de Cabara (Goat Meat Calulu) Origin: Angola | Fat Hen Quiche Origin: British |
| Aliter Ofellas (Roast Morsels, Another Way) Origin: Roman | Camarão na Abóbora (Prawns in Pumpkin Shells) Origin: Mozambique | Feuilles de Consoude Farcies (Stuffed Comfrey Leaves) Origin: France |
| Antiguan Curry Goat Origin: Antigua | Cameroonian Jollof Rice Origin: Cameroon | Ffowlyn Morganwg Rhost gyda Chaws a Pherlysiau (Roast Glamorgan Chicken with Cheese and Herbs) Origin: Welsh |
| Antiguan Rice and Peas Origin: Antigua | Capretto al Forno (Oven-roasted Kid Goat) Origin: Italy | Fig and Goat's Cheese Brioche Toasts Origin: Peru |
| Artolaganon (Fried Savoury Pasta) Origin: Roman | Cari Massale de Cabri (Goat Curry) Origin: Reunion | Fijian Goat Curry Origin: Fiji |
| Artolaganon II (Leavened Flatbread) Origin: Roman | Carne de Cebra Grealhado (Barbecued Goat Meat) Origin: Guinea-Bissau | Fijian Goat Curry 2 Origin: Fiji |
| Aruban Curried Goat Origin: Aruba | Cassava Life Origin: Sierra Leone | Gambian-style Okro Soup Origin: Gambia |
| Aruban Curry Goat Origin: Aruba | Caws Gafr gyda Betys a Llysiau Gwyllt (Goat's Cheese with Beetroot and Wild Herbs) Origin: Welsh (Patagonia) | Ghanaian Cabbage Stew Origin: Ghana |
| Börek Sauvage (Wild Greens Börek) Origin: France | Cayman Curry Goat Origin: Cayman Islands | Goat and Aubergine Kebabs Origin: Haiti |
| Bahamian Crab and Rice Origin: Saint Barthelemy | Charque (Bolivian Dried Meat) Origin: Bolivia | Goat Brochettes Origin: Rwanda |
| Bajan Curry Goat Origin: Barbados | Cheese and Sesame Balls Origin: Roman | Goat Curry Origin: Britain |
| Bajan Curry Powder Origin: Barbados | Cherry Tomato Bites Origin: British | Goat curry Origin: India |
| Balti Tandoori Keema Origin: Britain | Chichinga (Skewered Goat) Origin: Central African Republic | Goat Curry II Origin: Fusion |
| Bangladeshi Goat Curry Origin: Bangladesh | Chiles En Nogada (Stuffed Chillies in White Sauce) Origin: Mexico | Goat Curry with Potatoes Origin: Pakistan |
| Basto and Suugo Origin: Somalia | Chivo Guisado Liniero (Spicy Goat Meat Stew) Origin: Dominican Republic | Goat in the Burmese Style Origin: Fusion |
| Basto and Suugo Origin: Djibouti | Chivo Picante (Dominican Spicy Goat) Origin: Dominican Republic | Goat Meat and Root Vegetable Stew in Ale Origin: Britain |
| Beninese Goat Stew Origin: Benin | Citrus Goat Meat Stew Origin: Tanzania | Goat Meat Groundnut Soup Origin: Ghana |
| Bhindi Gosht (Pakistani Mutton and Okra Curry) Origin: Pakistan | Clay-baked Leg of Goat Origin: Britain | Goat Meat Pepper Soup with Calabash Nutmeg Origin: Nigeria |
| Bhojpur Mutton Curry Origin: India | Colombo de Chèvre (Goat Colombo Curry) Origin: Sint Maarten | Goat Meat Soup Origin: Liberia |
| Blossom-stuffed Pork Tenderloin Origin: American | Colombo de Chèvre (Goat Colombo Curry) Origin: Saint-Martin | Goat Meat Suya Origin: Nigeria |
| Bottle Masala Meatball Curry Origin: India | Copadia Haedina Sive Agnina (Choice Cuts of Kid or Lamb) Origin: Roman | Goat Mince Rissole Origin: Britain |
| Brewet of Almayn (Bruet of Almonds) Origin: England | Cornish Fish Pie Origin: England | Goat Water Origin: Antigua |
| Brochettes de Boeuf (Beef Kebabs) Origin: Rwanda | Curried Goat Origin: Jamaica | Goat Water Origin: Saint Kitts |
| Brunei Satay Origin: Brunei | Curry Chicken with Potatoes Origin: Trinidad | Goat's Cheese Muffins (Goat's Cheese Muffins) Origin: Britain |
| Bucellae cum Lacte Caprino (Bred Morsels with Goats' Milk) Origin: Roman | Dhaba Mutton Curry Origin: India | Gode Paest Origin: England |
| Burundi Brochettes Origin: Burundi | Dibi Origin: Gambia | Gongura Mamsam Origin: India |
| Cabri aux Gombos et Patates Douces (Goat with Okra and Sweet Potatoes) Origin: Senegal | Djibouti Sambusas Origin: Djibouti | |
| Cabri farci, façon afar (Stuffed Goat, Afar Style) Origin: Djibouti | Dominica Curried Goat Origin: Dominica |
Page 1 of 3