FabulousFusionFood's Bahamian Recipes Home Page
 The flag of The Bahamas (left) and the coat of arms of The Bahamas (right).
The flag of The Bahamas (left) and the coat of arms of The Bahamas (right).
Welcome to the summary page for FabulousFusionFood's Bahamian recipes, part of the Caribbean. This page provides links to all the Bahamian recipes presented on this site, with 20 recipes in total.
This is a continuation of an entire series of pages that will, I hope, allow my visitors to better navigate this site. As well as displaying recipes by name, country and region of origin I am now planning a whole series of pages where recipes can be located by meal type and main ingredient. This page gives a listing of all the Indian recipes added to this site.
The Bahamas, Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2.
Bahamian includes seafood such as fish, shellfish, lobster, crab, and conch, as well as tropical fruit, rice, peas, pigeon peas, and pork. Popular seasonings commonly used in dishes include chilies (hot pepper), lime, tomatoes, onions, garlic, allspice, ginger, cinnamon, rum, and coconut.
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and 88% of its population. The archipelagic country consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.
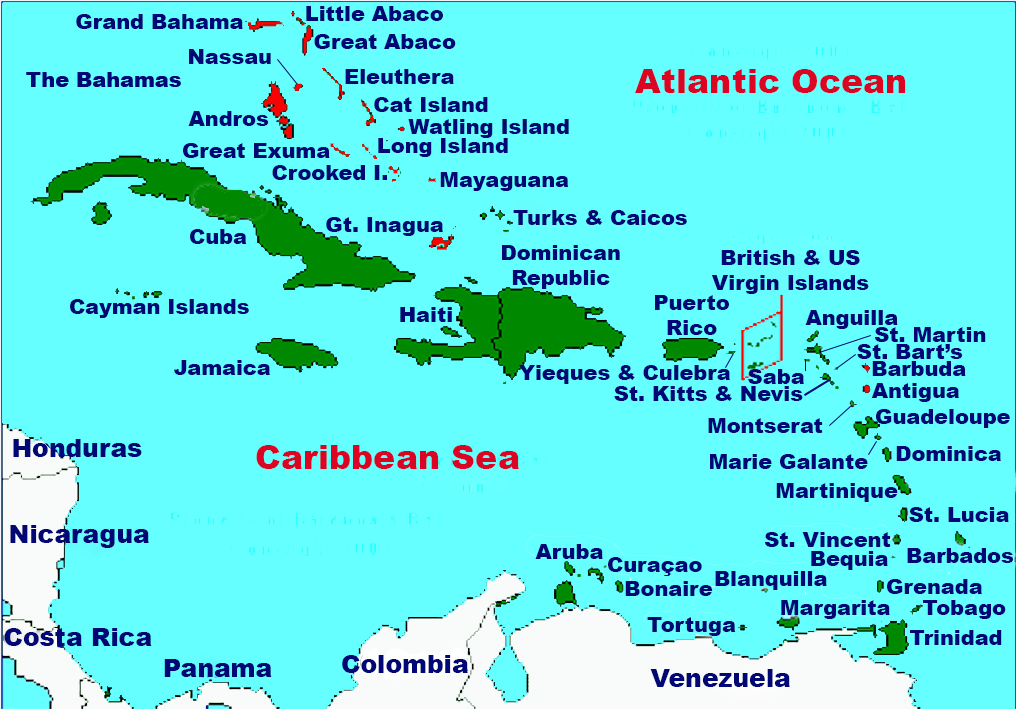 Location of The Bahamas in the Caribbean with the land mass of the
Location of The Bahamas in the Caribbean with the land mass of the
Bahamian islands picked out in red.The Bahama islands were inhabited by the Arawak and Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan-speaking Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making his first landfall in the 'New World' in 1492 when he landed on the island of San Salvador. Later, the Spanish shipped the native Lucayans to Hispaniola and enslaved them there, after which the Bahama islands were mostly deserted from 1513 until 1648, nearly all native Bahamians having been forcibly removed for enslavement or having died of diseases that Europeans brought with them from Europe. In 1649, English colonists from Bermuda, known as the Eleutheran Adventurers, settled on the island of Eleuthera.
The Bahamas became a British crown colony in 1718, when the British clamped down on piracy. After the American Revolutionary War, the Crown resettled thousands of American Loyalists to The Bahamas; they took enslaved people with them and established plantations on land grants. Enslaved Africans and their descendants constituted the majority of the population from this period on. The slave trade was abolished by the British in 1807. Although slavery in The Bahamas was not abolished until 1834, The Bahamas became a haven of manumission for African slaves, from outside the British West Indies, in 1818. Africans liberated from illegal slave ships were resettled on the islands by the Royal Navy, while some North American slaves and Seminoles escaped to The Bahamas from Florida. Bahamians were even known to recognise the freedom of enslaved people carried by the ships of other nations which reached The Bahamas. Today Black-Bahamians make up 90% of the population of 400,516.
The country gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1973, led by Sir Lynden O. Pindling. It shares its monarch with the other Commonwealth realms. The Bahamas has the fourteenth-largest gross domestic product per capita in the Americas. Its economy is based on tourism and offshore finance. Though the Bahamas is in the Lucayan Archipelago, and not on the Caribbean Sea, it is often considered part of the wider Caribbean region. The Bahamas is a full member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) but is not part of the CARICOM Single Market and Economy
The name Bahamas is derived from the Lucayan name Bahama ('large upper middle island'), used by the indigenous Taíno people for the island of Grand Bahama. Tourist guides often state that the name comes from the Spanish baja mar ('shallow sea'). Wolfgang Ahrens of York University argues that this is a folk etymology. Alternatively, Bahama may have been derived from Guanahaní, a local name of unclear meaning.
First attested on the c. 1523 Turin Map, Bahama originally referred to Grand Bahama alone but was used inclusively in English by 1670. Toponymist Isaac Taylor argues that the name was derived from Bimani (Bimini), which Spaniards in Haiti identified with Palombe, a legendary place where John Mandeville's Travels said there was a fountain of youth.
The Bahamas is one of only two countries whose official names start with the article 'the'. (The other is The Gambia.) The usage likely arose because the name also refers to the islands, a geographical feature that would take a definite article.
Many specialty dishes are available at roadside stands, beach side, and in fine dining establishments. In contrast to the offerings in the city of Nassau and the many hotels, 'shack' type food stands/restaurants (including Goldies and Twin Brothers) are located at Arawak Cay on West Bay Street about 15 minutes from downtown Nassau and 25 minutes from Atlantis Paradise Island resort. This is a very organized and safe place to enjoy fresh seafood and all local Bahamian dishes. Travellers Rest Restaurant, in Nassau, is known for serving authentic 'local' foods.
This is a continuation of an entire series of pages that will, I hope, allow my visitors to better navigate this site. As well as displaying recipes by name, country and region of origin I am now planning a whole series of pages where recipes can be located by meal type and main ingredient. This page gives a listing of all the Indian recipes added to this site.
The Bahamas, Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2.
Bahamian includes seafood such as fish, shellfish, lobster, crab, and conch, as well as tropical fruit, rice, peas, pigeon peas, and pork. Popular seasonings commonly used in dishes include chilies (hot pepper), lime, tomatoes, onions, garlic, allspice, ginger, cinnamon, rum, and coconut.
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and 88% of its population. The archipelagic country consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.
 Location of The Bahamas in the Caribbean with the land mass of the
Location of The Bahamas in the Caribbean with the land mass of theBahamian islands picked out in red.
The Bahamas became a British crown colony in 1718, when the British clamped down on piracy. After the American Revolutionary War, the Crown resettled thousands of American Loyalists to The Bahamas; they took enslaved people with them and established plantations on land grants. Enslaved Africans and their descendants constituted the majority of the population from this period on. The slave trade was abolished by the British in 1807. Although slavery in The Bahamas was not abolished until 1834, The Bahamas became a haven of manumission for African slaves, from outside the British West Indies, in 1818. Africans liberated from illegal slave ships were resettled on the islands by the Royal Navy, while some North American slaves and Seminoles escaped to The Bahamas from Florida. Bahamians were even known to recognise the freedom of enslaved people carried by the ships of other nations which reached The Bahamas. Today Black-Bahamians make up 90% of the population of 400,516.
The country gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1973, led by Sir Lynden O. Pindling. It shares its monarch with the other Commonwealth realms. The Bahamas has the fourteenth-largest gross domestic product per capita in the Americas. Its economy is based on tourism and offshore finance. Though the Bahamas is in the Lucayan Archipelago, and not on the Caribbean Sea, it is often considered part of the wider Caribbean region. The Bahamas is a full member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) but is not part of the CARICOM Single Market and Economy
The name Bahamas is derived from the Lucayan name Bahama ('large upper middle island'), used by the indigenous Taíno people for the island of Grand Bahama. Tourist guides often state that the name comes from the Spanish baja mar ('shallow sea'). Wolfgang Ahrens of York University argues that this is a folk etymology. Alternatively, Bahama may have been derived from Guanahaní, a local name of unclear meaning.
First attested on the c. 1523 Turin Map, Bahama originally referred to Grand Bahama alone but was used inclusively in English by 1670. Toponymist Isaac Taylor argues that the name was derived from Bimani (Bimini), which Spaniards in Haiti identified with Palombe, a legendary place where John Mandeville's Travels said there was a fountain of youth.
The Bahamas is one of only two countries whose official names start with the article 'the'. (The other is The Gambia.) The usage likely arose because the name also refers to the islands, a geographical feature that would take a definite article.
Food and Cuisine:
Bahamian cuisine refers to the foods and beverages of The Bahamas. It includes seafood such as fish, shellfish, lobster, crab, and conch, as well as tropical fruit, rice, peas, pigeon peas, and pork. Popular seasonings commonly used in dishes include chilies (hot pepper), lime, tomatoes, onions, garlic, allspice, ginger, cinnamon, rum, and coconut. Rum-based beverages are popular on the islands. Since the Bahamas consist of a multitude of islands, notable culinary variations exist.Many specialty dishes are available at roadside stands, beach side, and in fine dining establishments. In contrast to the offerings in the city of Nassau and the many hotels, 'shack' type food stands/restaurants (including Goldies and Twin Brothers) are located at Arawak Cay on West Bay Street about 15 minutes from downtown Nassau and 25 minutes from Atlantis Paradise Island resort. This is a very organized and safe place to enjoy fresh seafood and all local Bahamian dishes. Travellers Rest Restaurant, in Nassau, is known for serving authentic 'local' foods.
The alphabetical list of all the Bahamian recipes on this site follows, (limited to 100 recipes per page). There are 20 recipes in total:
Page 1 of 1
| Bahamian Baked Macaroni and Cheese Origin: Bahamas | Baked Snapper Origin: Bahamas | Loquat Leather Origin: Bahamas |
| Bahamian Bread Pudding Origin: Bahamas | Cassava Pone Origin: Bahamas | Mauby Origin: Bahamas |
| Bahamian Cracked Conch Origin: Bahamas | Conkies Origin: Bahamas | Pineapple Coleslaw Origin: Bahamas |
| Bahamian Ginger Beer Origin: Bahamas | Crab and Rice Origin: Bahamas | Salt Cod and Sweet Potato Fish Cakes Origin: Bahamas |
| Bahamian Lobster Curry Origin: Bahamas | Guava Juice Origin: Bahamas | Salt Cod Fish Cakes Origin: Bahamas |
| Bajan Chicken and Coconut Curry Origin: Bahamas | Island Fish Tea Origin: Bahamas | Sorrel Drink Origin: Bahamas |
| Bajan Spice Blend Origin: Bahamas | Loquat Jam Origin: Bahamas |
Page 1 of 1