FabulousFusionFood's Hawaiian Recipes Home Page
 The flag of Hawaii (left) and the coat of arms of Hawaii (right).
The flag of Hawaii (left) and the coat of arms of Hawaii (right).
Welcome to the summary page for FabulousFusionFood's Hawaii recipes, part of Oceania. This page provides links to all the Hawaiian recipes presented on this site, with 16 recipes in total.
This is a continuation of an entire series of pages that will, I hope, allow my visitors to better navigate this site. As well as displaying recipes by name, country and region of origin I am now planning a whole series of pages where recipes can be located by meal type and main ingredient. This page gives a listing of all the Indian recipes added to this site.
The cuisine of Hawaii is a fusion of many foods brought by immigrants to the Hawaiian Islands, including the earliest Polynesians and Native Hawaiian cuisine, and American, Chinese, Filipino, Japanese, Korean, Polynesian, Puerto Rican, and Portuguese origins.
These recipes, for the major part, originate in Hawaii. Otherwise they are fusion recipes with major Hawaiian influences.
Hawaii, Hawaiian: Hawaiʻi is an island state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the U.S. mainland. It is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics. It also hosts 10 out of 14 climates - the highest for any country subdivision - and is one of two U.S. states with a tropical climate.
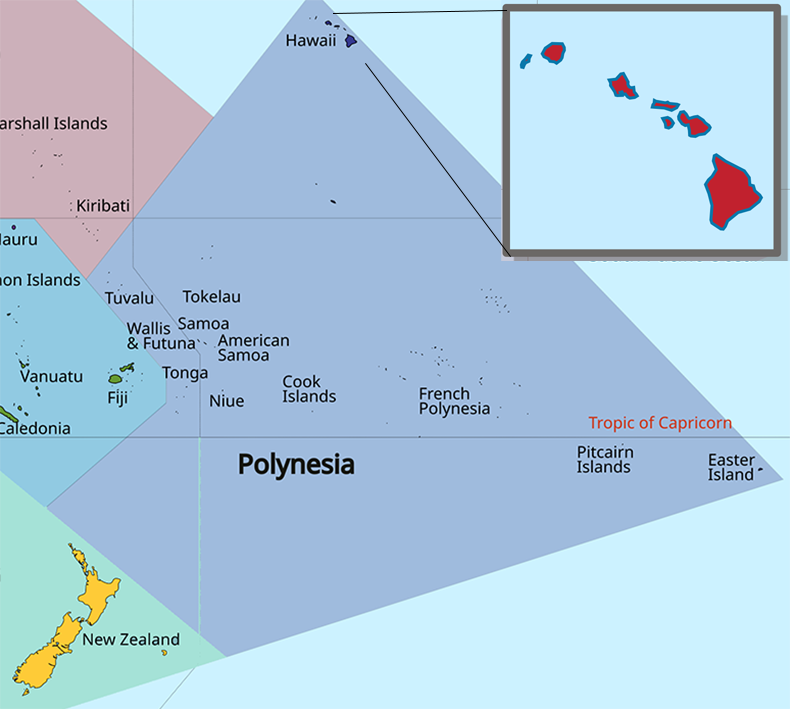 The image above shows Hawaii in relation to Polynesia, with the Hawaiian islands expanded.Hawaii consists of 137 volcanic islands that comprise almost the entire Hawaiian archipelago (the exception, which is outside the state, is Midway Atoll). Spanning 1,500 miles (2,400 km), the state is physiographically and ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania. Hawaii's ocean coastline is consequently the fourth-longest in the U.S., at about 750 miles (1,210 km). The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niʻihau, Kauaʻi, Oʻahu, Molokaʻi, Lānaʻi, Kahoʻolawe, Maui, and Hawaiʻi, after which the state is named; the latter is often called the 'Big Island' or 'Hawaii Island' to avoid confusion with the state or archipelago. The uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands make up most of the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the largest protected area in the U.S. and the fourth-largest in the world.
The image above shows Hawaii in relation to Polynesia, with the Hawaiian islands expanded.Hawaii consists of 137 volcanic islands that comprise almost the entire Hawaiian archipelago (the exception, which is outside the state, is Midway Atoll). Spanning 1,500 miles (2,400 km), the state is physiographically and ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania. Hawaii's ocean coastline is consequently the fourth-longest in the U.S., at about 750 miles (1,210 km). The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niʻihau, Kauaʻi, Oʻahu, Molokaʻi, Lānaʻi, Kahoʻolawe, Maui, and Hawaiʻi, after which the state is named; the latter is often called the 'Big Island' or 'Hawaii Island' to avoid confusion with the state or archipelago. The uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands make up most of the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the largest protected area in the U.S. and the fourth-largest in the world.
Settled by Polynesians sometime between 1000 and 1200 CE, Hawaii was home to numerous independent chiefdoms. In 1778, British explorer James Cook was the first known non-Polynesian to arrive at the archipelago; early British influence is reflected in the state flag, which bears a Union Jack. An influx of European and American explorers, traders, and whalers soon arrived, leading to the decimation of the once-isolated indigenous community through the introduction of diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, smallpox, and measles; the native Hawaiian population declined from between 300,000 and one million to less than 40,000 by 1890. Hawaii became a unified, internationally recognized kingdom in 1810, remaining independent until American and European businessmen overthrew the monarchy in 1893; this led to annexation by the U.S. in 1898. As a strategically valuable U.S. territory, Hawaii was attacked by Japan on December 7, 1941, which brought it global and historical significance, and contributed to America's entry into World War II. Hawaii is the most recent state to join the union, on August 21, 1959. In 1993, the U.S. government formally apologized for its role in the overthrow of Hawaii's government, which had spurred the Hawaiian sovereignty movement and has led to ongoing efforts to obtain redress for the indigenous population.
The State of Hawaii derives its name from the name of its largest island, Hawaiʻi. A common explanation of the name of Hawaiʻi is that it was named for Hawaiʻiloa, a figure from Hawaiian oral tradition. He is said to have discovered the islands when they were first settled.
The Hawaiian language word Hawaiʻi is very similar to Proto-Polynesian Sawaiki, with the reconstructed meaning 'homeland'. Cognates of Hawaiʻi are found in other Polynesian languages, including Māori (Hawaiki), Rarotongan (ʻAvaiki) and Samoan (Savaiʻi). According to linguists Pukui and Elbert, 'elsewhere in Polynesia, Hawaiʻi or a cognate is the name of the underworld or of the ancestral home, but in Hawaii, the name has no meaning'.
This is a continuation of an entire series of pages that will, I hope, allow my visitors to better navigate this site. As well as displaying recipes by name, country and region of origin I am now planning a whole series of pages where recipes can be located by meal type and main ingredient. This page gives a listing of all the Indian recipes added to this site.
The cuisine of Hawaii is a fusion of many foods brought by immigrants to the Hawaiian Islands, including the earliest Polynesians and Native Hawaiian cuisine, and American, Chinese, Filipino, Japanese, Korean, Polynesian, Puerto Rican, and Portuguese origins.
These recipes, for the major part, originate in Hawaii. Otherwise they are fusion recipes with major Hawaiian influences.
Hawaii, Hawaiian: Hawaiʻi is an island state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the U.S. mainland. It is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics. It also hosts 10 out of 14 climates - the highest for any country subdivision - and is one of two U.S. states with a tropical climate.
 The image above shows Hawaii in relation to Polynesia, with the Hawaiian islands expanded.
The image above shows Hawaii in relation to Polynesia, with the Hawaiian islands expanded.Settled by Polynesians sometime between 1000 and 1200 CE, Hawaii was home to numerous independent chiefdoms. In 1778, British explorer James Cook was the first known non-Polynesian to arrive at the archipelago; early British influence is reflected in the state flag, which bears a Union Jack. An influx of European and American explorers, traders, and whalers soon arrived, leading to the decimation of the once-isolated indigenous community through the introduction of diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, smallpox, and measles; the native Hawaiian population declined from between 300,000 and one million to less than 40,000 by 1890. Hawaii became a unified, internationally recognized kingdom in 1810, remaining independent until American and European businessmen overthrew the monarchy in 1893; this led to annexation by the U.S. in 1898. As a strategically valuable U.S. territory, Hawaii was attacked by Japan on December 7, 1941, which brought it global and historical significance, and contributed to America's entry into World War II. Hawaii is the most recent state to join the union, on August 21, 1959. In 1993, the U.S. government formally apologized for its role in the overthrow of Hawaii's government, which had spurred the Hawaiian sovereignty movement and has led to ongoing efforts to obtain redress for the indigenous population.
The State of Hawaii derives its name from the name of its largest island, Hawaiʻi. A common explanation of the name of Hawaiʻi is that it was named for Hawaiʻiloa, a figure from Hawaiian oral tradition. He is said to have discovered the islands when they were first settled.
The Hawaiian language word Hawaiʻi is very similar to Proto-Polynesian Sawaiki, with the reconstructed meaning 'homeland'. Cognates of Hawaiʻi are found in other Polynesian languages, including Māori (Hawaiki), Rarotongan (ʻAvaiki) and Samoan (Savaiʻi). According to linguists Pukui and Elbert, 'elsewhere in Polynesia, Hawaiʻi or a cognate is the name of the underworld or of the ancestral home, but in Hawaii, the name has no meaning'.
Hawaiian Cuisine:
The cuisine of Hawaii is a fusion of many foods brought by immigrants to the Hawaiian Islands, including the earliest Polynesians and Native Hawaiian cuisine, and American, Chinese, Filipino, Japanese, Korean, Polynesian, Puerto Rican, and Portuguese origins. Plant and animal food sources are imported from around the world for agricultural use in Hawaii. Poi, a starch made by pounding taro, is one of the traditional foods of the islands. Many local restaurants serve the ubiquitous plate lunch, which features two scoops of rice, a simplified version of American macaroni salad and a variety of toppings including hamburger patties, a fried egg, and gravy of a loco moco, Japanese style tonkatsu or the traditional lūʻau favorites, including kālua pork and laulau. Spam musubi is an example of the fusion of ethnic cuisine that developed on the islands among the mix of immigrant groups and military personnel. In the 1990s, a group of chefs developed Hawaii regional cuisine as a contemporary fusion cuisine.The alphabetical list of all the Hawaiian recipes on this site follows, (limited to 100 recipes per page). There are 16 recipes in total:
Page 1 of 1
| Ahi Poke Bowl Origin: Hawaii | Hawaiian Brunch Pizza Origin: Hawaii | Shoyu Chicken Origin: Hawaii |
| Banana Pineapple Bread Origin: Hawaii | Mochi Doughnuts Origin: Hawaii | Spam Musubi Origin: Hawaii |
| Breadfruit with Coconut Milk Origin: Hawaii | Mochi Pancakes Origin: Hawaii | Ulu (Hawaiian Roasted Breadfruit) Origin: Hawaii |
| Chicken Pupus Origin: Hawaii | Nori-wrapped Mochiko Chicken Origin: Hawaii | Watermelon Otai Origin: Hawaii |
| Easy Shoyu Chicken Origin: Hawaii | Pacific-style Coconut Rice Origin: Hawaii | |
| Haupia (Hawaiian Coconut Pudding) Origin: Hawaii | Saimin (Hawaiian Noodle Soup) Origin: Hawaii |
Page 1 of 1