FabulousFusionFood's Mauritian Recipes Home Page
 The flag of Mauritius (left) and the coat of arms of Mauritius (right).
The flag of Mauritius (left) and the coat of arms of Mauritius (right).
Welcome to the summary page for FabulousFusionFood's Mauritian recipes, part of East Africa. This page provides links to all the Mauritian recipes presented on this site, with 47 recipes in total.
These recipes, for the major part, originate in Mauritius. Otherwise they are fusion recipes with major Mauritian influences.
Mauritius officially the Republic of Mauritius; French: République de Maurice; Morisyen: Repiblik Moris, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean, about 2,000 kilometres (1,100 nautical miles) off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga, and St. Brandon (Cargados Carajos shoals). The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion (a French overseas department), are part of the Mascarene Islands. The main island of Mauritius, where the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis. The country spans 2,040 square kilometres (790 sq mi) and has an exclusive economic zone covering 2,300,000 square kilometres (670,000 square nautical miles).
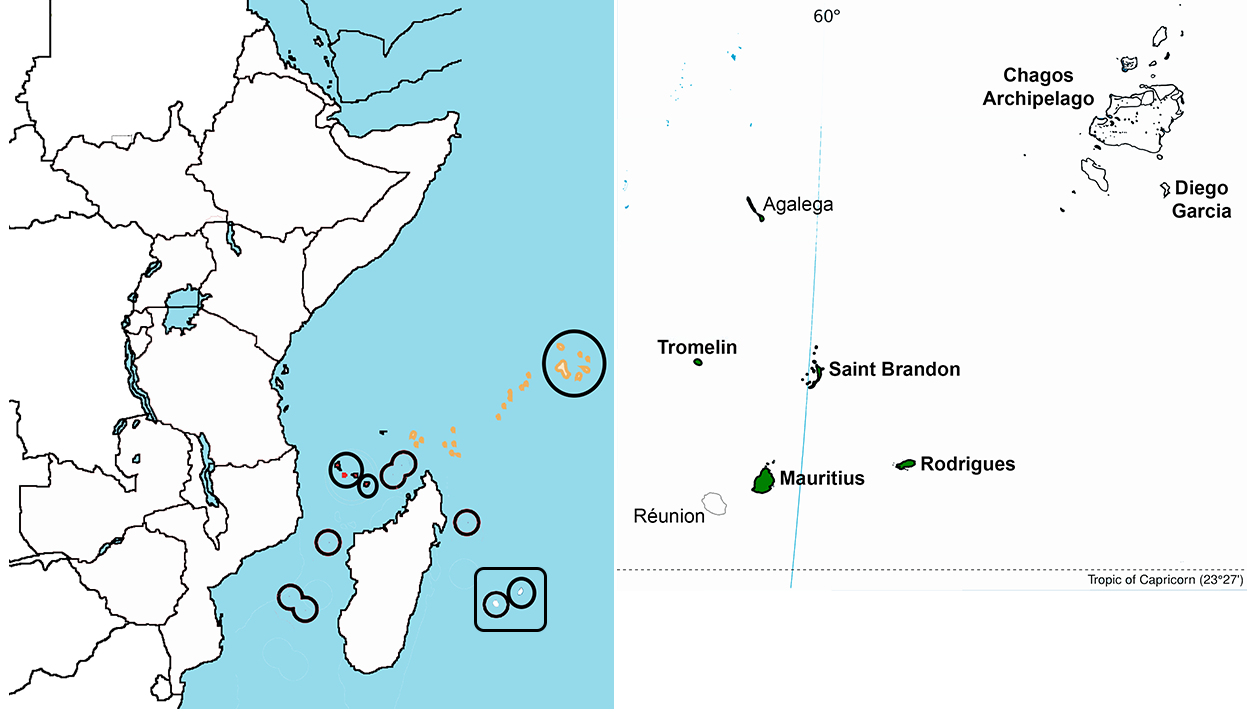 The image above shows a view of Mauritius (boxed) in relation to East Africa,
The image above shows a view of Mauritius (boxed) in relation to East Africa,
with an expanded view of the Mauritian islands to the right.Based on the only surviving map of the Portuguese discoveries dated 1502 called the Cantino planisphere, it is generally accepted that Arab sailors first discovered the uninhabited island, around 975, naming it Dina Arobi. In 1507, Portuguese sailors visited the uninhabited island with the island appearing with the Portuguese names Cirne or Do-Cerne on early Portuguese maps. A Dutch fleet, under the command of Admiral Van Warwyck, landed at what is now the Grand Port District and took possession of the island in 1598, renaming the uninhabited islands after Maurice, Prince of Orange. A succession of short-lived Dutch attempts at permanent settlement took place over a century with the aim of exploiting the local ebony forests, establishing a consistent sugar and arrack production using cane plant cuttings imported from Java together with over three hundred Malagasy slaves, before abandoning their efforts. France took the uninhabited island in 1715, renaming the island 'Isle de France'. In 1810, the United Kingdom seized the island, and four years later, under the Treaty of Paris, France ceded Mauritius and its dependencies to the United Kingdom. The British colony of Mauritius now included Rodrigues, Agaléga, St. Brandon, the Chagos Archipelago, and, until 1906, the Seychelles. Mauritius and France dispute sovereignty over the island of Tromelin. The treaty failed to mention it specifically. Mauritius became the British Empire's main sugar-producing colony and remained a primarily sugar-dominated plantation-based colony until independence, in 1968.
Given its geographic location and colonial past, the people of Mauritius are diverse in ethnicity, culture, language and faith. It is the only country in Africa where Hinduism is the most practised religion. Indo-Mauritians make up the bulk of the population with significant Creole, Sino-Mauritian and Franco-Mauritian minorities. The island's government is closely modelled on the Westminster parliamentary system with Mauritius highly ranked for economic and political freedom being listed by the Economist's Democracy Index as the only country in Africa with full democracy. Mauritius has a high Human Development Index, and the World Bank classifies it as a high-income economy. It is amongst the most competitive and most developed economies in the African region. The country is a welfare state. The government provides free universal healthcare, free education up through the tertiary level and free public transportation for students, senior citizens, and the disabled. Mauritius is consistently ranked as the most peaceful country in Africa.
In 1965, the UK split off the Chagos Archipelago from Mauritian territory to create the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT). The local population was forcibly expelled and the largest island, Diego Garcia, was leased to the United States. Ruling on the sovereignty dispute between Mauritius and the UK, the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea has ordered the return of the Chagos Islands to Mauritius.
Etymology: The first historical evidence of the existence of the island now known as Mauritius is on a 1502 map called the Cantino planisphere which was smuggled out of Portugal, for the Duke of Ferrara, by the Italian 'spy' Alberto Cantino. On this purloined copy of a Portuguese map, Mauritius bore the name Dina Arobi (likely Arabic: دنية عروبي Daniyah ‘Arūbi or corruption of دبية عروبي Dībah ‘Arūbi). In 1507, Portuguese sailors visited the uninhabited island after being blown off course from their route to India via the Mozambique channel. The island appears with the Portuguese names Cirne (a typographical error where the 's' of the Portuguese 'Cisne' (Swan) became an 'r') or Do-Cerne (typo of 'do Cisne' meaning 'of' or 'belonging to the Swan') on early Portuguese maps, almost certainly from the name of a ship called Cisne which was captained by Diogo Fernandes Pereira in the 1507 expedition which discovered Mauritius and Rodrigues which he called ilha de Diogo Fernandes but poorly transcribed by non-Portuguese speakers as Domigo Friz or Domingo Frias. Diogo Fernandes Pereira may have been the first European to sail east of Madagascar island ('outer route' to the East Indies) rather than through the perceived safer route through the Mozambique channel, following the East African shore line.
In 1598, a Dutch squadron under Admiral Wybrand van Warwyck landed at Grand Port and named the island Mauritius, in honour of Prince Maurice van Nassau, stadtholder of the Dutch Republic. Later the island became a French colony and was renamed Isle de France. On 3 December 1810, the French surrendered the island to the United Kingdom during the Napoleonic Wars. Under British rule, the island's name reverted to Mauritius /məˈrɪʃəs/ ⓘ. Mauritius is also commonly known as Maurice (pronounced [mɔˈʁis]) and Île Maurice in French, Moris (pronounced [moʁis]) in Mauritian Creole.
These recipes, for the major part, originate in Mauritius. Otherwise they are fusion recipes with major Mauritian influences.
Mauritius officially the Republic of Mauritius; French: République de Maurice; Morisyen: Repiblik Moris, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean, about 2,000 kilometres (1,100 nautical miles) off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga, and St. Brandon (Cargados Carajos shoals). The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion (a French overseas department), are part of the Mascarene Islands. The main island of Mauritius, where the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis. The country spans 2,040 square kilometres (790 sq mi) and has an exclusive economic zone covering 2,300,000 square kilometres (670,000 square nautical miles).
 The image above shows a view of Mauritius (boxed) in relation to East Africa,
The image above shows a view of Mauritius (boxed) in relation to East Africa,with an expanded view of the Mauritian islands to the right.
Given its geographic location and colonial past, the people of Mauritius are diverse in ethnicity, culture, language and faith. It is the only country in Africa where Hinduism is the most practised religion. Indo-Mauritians make up the bulk of the population with significant Creole, Sino-Mauritian and Franco-Mauritian minorities. The island's government is closely modelled on the Westminster parliamentary system with Mauritius highly ranked for economic and political freedom being listed by the Economist's Democracy Index as the only country in Africa with full democracy. Mauritius has a high Human Development Index, and the World Bank classifies it as a high-income economy. It is amongst the most competitive and most developed economies in the African region. The country is a welfare state. The government provides free universal healthcare, free education up through the tertiary level and free public transportation for students, senior citizens, and the disabled. Mauritius is consistently ranked as the most peaceful country in Africa.
In 1965, the UK split off the Chagos Archipelago from Mauritian territory to create the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT). The local population was forcibly expelled and the largest island, Diego Garcia, was leased to the United States. Ruling on the sovereignty dispute between Mauritius and the UK, the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea has ordered the return of the Chagos Islands to Mauritius.
Etymology: The first historical evidence of the existence of the island now known as Mauritius is on a 1502 map called the Cantino planisphere which was smuggled out of Portugal, for the Duke of Ferrara, by the Italian 'spy' Alberto Cantino. On this purloined copy of a Portuguese map, Mauritius bore the name Dina Arobi (likely Arabic: دنية عروبي Daniyah ‘Arūbi or corruption of دبية عروبي Dībah ‘Arūbi). In 1507, Portuguese sailors visited the uninhabited island after being blown off course from their route to India via the Mozambique channel. The island appears with the Portuguese names Cirne (a typographical error where the 's' of the Portuguese 'Cisne' (Swan) became an 'r') or Do-Cerne (typo of 'do Cisne' meaning 'of' or 'belonging to the Swan') on early Portuguese maps, almost certainly from the name of a ship called Cisne which was captained by Diogo Fernandes Pereira in the 1507 expedition which discovered Mauritius and Rodrigues which he called ilha de Diogo Fernandes but poorly transcribed by non-Portuguese speakers as Domigo Friz or Domingo Frias. Diogo Fernandes Pereira may have been the first European to sail east of Madagascar island ('outer route' to the East Indies) rather than through the perceived safer route through the Mozambique channel, following the East African shore line.
In 1598, a Dutch squadron under Admiral Wybrand van Warwyck landed at Grand Port and named the island Mauritius, in honour of Prince Maurice van Nassau, stadtholder of the Dutch Republic. Later the island became a French colony and was renamed Isle de France. On 3 December 1810, the French surrendered the island to the United Kingdom during the Napoleonic Wars. Under British rule, the island's name reverted to Mauritius /məˈrɪʃəs/ ⓘ. Mauritius is also commonly known as Maurice (pronounced [mɔˈʁis]) and Île Maurice in French, Moris (pronounced [moʁis]) in Mauritian Creole.
Food and Cuisine:
Mauritian cuisine is a combination of Indian, Creole, French and Chinese, with many dishes unique to the island. Spices are also a major component of Mauritian cuisine. There is a local variant of Persian falooda, locally known as alouda, which is a cold beverage made with milk, basil seeds, and agar-agar jelly. Locally made French pastry and bread are sold in most localities. Popular hawker meals include a wrap called dholl puri, rice-based biryani and gâteau pimentThe alphabetical list of all the Mauritian recipes on this site follows, (limited to 100 recipes per page). There are 47 recipes in total:
Page 1 of 1
| Biriani de Poulet (Chicken Biriani) Origin: Mauritius | Egg Roll Wrappers Origin: Mauritius | Pâtissons Farcis (Stuffed Squash) Origin: Mauritius |
| Bouillon de Crabes (Swimmer Crab Bouillon) Origin: Mauritius | Fish Vindaye Origin: Mauritius | Peanut Rougail Origin: Mauritius |
| Bouillon de Petits Crabes (Stew of Small Crabs) Origin: Mauritius | Fricassée de Coq (Chicken Fricassee) Origin: Mauritius | Poisson aux Fines Herbes (Herbed Fish) Origin: Mauritius |
| Cari Dholl (Yellow Split Pea Curry) Origin: Mauritius | Gateaux Piments (Chilli Cakes) Origin: Mauritius | Poisson Salé (Salt Fish) Origin: Mauritius |
| Cari Ourite (Octopus Curry) Origin: Mauritius | Gato arouille (Taro Fritters) Origin: Mauritius | Poulet Créole (Creole Chicken) Origin: Mauritius |
| Cari Poisson (Mauritian Fish Curry) Origin: Mauritius | Gratin de Morue (Salt Cod Gratin) Origin: Mauritius | Rôti de Porc à l'Ananas (Roast Pork with Pineapple) Origin: Mauritius |
| Cari Poisson (Fish Curry) Origin: Mauritius | Haiken (Chicken and Prawn Egg Rolls) Origin: Mauritius | Rougail Saucisse (Sausage Rougail) Origin: Mauritius |
| Carri Masala Poule Mauricien (Mauritian Chicken Curry) Origin: Mauritius | Kalya de Poulet (Chicken Kalya) Origin: Mauritius | Rougaille Boudin (Black Pudding in Tomato Sauce) Origin: Mauritius |
| Carri Tripes Gros Pois (Butter Bean and Tripe Curry) Origin: Mauritius | Lamb with Spinach Origin: Mauritius | Rougaille de Poisson Salé (Salted Fish Rougaille) Origin: Mauritius |
| Cassoulet Mauricien (Mauritian Cassoulet) Origin: Mauritius | Le Chou au Beurre (Buttered Cabbage) Origin: Mauritius | Salade Chou Chou (Chako Salad) Origin: Mauritius |
| Colombo d'Agneau à la Mauricienne (Mauritian-style Colombo of Lamb) Origin: Mauritius | Mauritian Colombo Chicken Curry Origin: Mauritius | Salmi Poulet Mauriticien (Chicken Mauritius) Origin: Mauritius |
| Curry de Boeuf (Beef Curry) Origin: Mauritius | Mauritian Curry Masala Origin: Mauritius | Satini Mangue Vert (Mauritian Mango Chutney) Origin: Mauritius |
| Curry de Boeuf au Yaourt (Beef Curry with Yoghurt) Origin: Mauritius | Mauritian Mayonnaise Origin: Mauritius | Thon Curry Moutarde à la Mauricienne (Mauritian-style Tuna Mustard Curry) Origin: Mauritius |
| Daube de Thon (Tuna Daube) Origin: Mauritius | Mauritian Poudre de Colombo Origin: Mauritius | Travers de Porc Grillé (Barbecued Ribs of Pork) Origin: Mauritius |
| Dholl Origin: Mauritius | Mauritian Prawn Curry Origin: Mauritius | White Cabbage Salad Origin: Mauritius |
| Dholl Pooris Origin: Mauritius | Mulku (Murukku) Origin: Mauritius |
Page 1 of 1